The Collision of Minimally Invasive Techniques with Maxillofacial Surgery
The so-called minimally invasive surgery refers to the advanced surgical mode in which modern photoelectric imaging system, micro-surgical device and energy generation equipment, replace traditional open operation with endoscopic technology, and precision controlled surgical instruments with traditional scalpel to complete the diagnosis and treatment of lesions through tiny wounds.
Maxillofacial surgery is an important branch of oral medicine for the surgical treatment of cranial and maxillofacial facial bones, soft tissues and temporomandibular joints.
According to the surgical symptoms and treatment purpose can be divided into the following categories:
1. Trauma Repair Surgery
- Treatment range: facial fracture
- Typical surgery: open reduction and internal fixation of the fracture
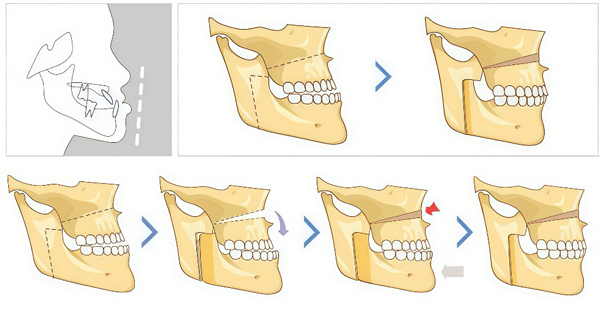
2. Orthognathic Surgery
- Treatment range: jaw development deformity
- Typical surgical method: type Le Fort I osteotomy, lost split osteotomy
3. Tumor Resection and Reconstructive Surgery
- Treatment range: jaw bone cystic lesions, benign and malignant tumors
- Typical surgical method: lesion enlargement resection combined with vascularized free tissue flap grafting
4. Temporomandibular Joint Surgery
- Treatment scope: joint ankylosis, structural disorder
- Typical surgical methods: joint disc reduction, joint molding
Important structures such as trigeminal nerve branches, facial nerve and external carotid artery are centrally distributed in the maxillofacial area. Traditional surgery is easy to cause nerve damage and vascular bleeding. At the same time, the incision scar formed after the traditional surgery is more obvious, while the minimally invasive technology can realize the incision concealment and non-trace healing. Therefore, the application of minimally invasive techniques is important for maxillofacial surgery.
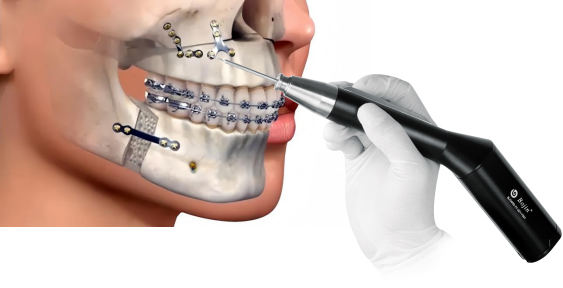
Application of Micro Power Tools in Minimally Invasive Maxillofacial Surgery
1. Bone Cutting and Plastic Surgery:
- Zygomatic and Mandibular Plastic Surgery: Micro bone drills and bone saws can be used to precisely cut bones and reshape bone contours through oral or small skin incisions, avoiding scars and nerve damage caused by traditional large incisions
- Fracture Reduction and Fixation: In complex fractures such as zygomatic arch and mandible, micro power tools can finely polish the bone surface, assist in reduction, and cooperate with micro titanium plate fixation to reduce intraoperative bleeding
2. Neurodecompression Technique: For facial nerve compression (such as Bell’s palsy), micro drills can be used with endoscopic assistance to remove bone (such as temporal bone) that compresses the nerve, avoiding damage to surrounding soft tissues
3. Dental Implantation and Bone Augmentation:
- Preparation of Implant Cavity: Micro implant drill bit (diameter can be less than 2mm) reduces bone thermal damage and improves initial stability of the implant by accurately controlling the speed and torque
- Bone Augmentation Surgery: used in bone splitting or bone compression surgery to increase bone mass while preserving autogenous bone activity, promoting bone regeneration
4. Endoscopic Assisted Surgery:
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Surgery: Through endoscopic channels, micro power tools can clean joint cavity adhesions, repair joint discs, or grind bone spurs to improve joint function
- Salivary Gland Stone Extraction: Micro drills are used to crush stones in the submandibular gland or parotid duct, avoiding gland resection
5. Tumor Resection and Biopsy:
- Removal of Jaw Cysts and Small Tumors: Through minimally invasive approaches, precise removal of lesions and preservation of surrounding healthy bone tissue are achieved, reducing the risk of postoperative deformities
Advantage of Minimally Invasive Techniques
1. Clinical Advantage of Functional Recovery
2. Multi-dimensional Improvement in Patient Benefit
- Physiological Level: the blood loss was <50ml (traditional surgery> 200ml), and the hospital stay was reduced to 1-3 days (traditional 5-7 days)
- Psychological Level: the wound is invisible, and the recovery time of social activities is 2-3 times earlier
- Economic Benefits: reduced cost of comprehensive treatment
3. Innovation at the Operational Level
- Improved visualization ability
- Operation accuracy breakthrough
- Complex surgery simplified
With the continuous innovation of technology, minimally invasive maxillofacial surgery will continue to develop in the direction of precision, personalization and intelligence, to provide safer and more effective treatment plans for patients.
